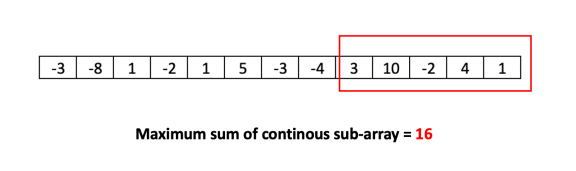
Kadane’s algorithm – finding maximum sum in contigous sub-array
Want to share your content on R-bloggers? click here if you have a blog, or here if you don't.
Great algorithm for analyzing timeseries data or array of numbers.
An algorithm for finding the contiguous subarray within a one-dimensional array of numbers that has the largest sum. It is called Kadane’s algorithm.
How does the algorithm work? It looks for a global maximum of positive-sum on any sub-array, regardless of its starting position or its length. Numbers must be next or together in a sequence (without any number left out).
With formula as: local_maximum at index i is the maximum of A[i] and the sum of A[i] and local_maximum at index i-1. So, you calculate the sum of every possible subarray ending with the element array[n-1]. Then, we would calculate the sum of every possible subarray ending with array[n-2], array[n-3] and so on up to array[0].
With a simple function we can iterate through the array (vector) of values:
#sample vector
v <- c(-3,-8, 1, -2, 1, 5, -3, -4, 3, 10, -2, 4, 1)
kadane <- function(v){
max_so_far = -999999999999999 #some obnoxiously big number
max_ending_here = 0
for (i in 1:length(v)) {
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + v[i]
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here ){
max_so_far = max_ending_here
}
if (max_ending_here < 0) {
max_ending_here = 0
}
}
return (max_so_far)
}
Run the function with:
# run the function kadane(v)
The function can also return the starting and ending positions of the array.
kadane_with_position <- function(v){
max_so_far = -999999999999999 #some obnoxiously big number
max_ending_here = 0
subarray_start = 0
subarray_end = 0
int_s = 0
for (i in 1:length(v)) {
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + v[i]
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here ){
max_so_far = max_ending_here
subarray_start = int_s
subarray_end = i
}
if (max_ending_here < 0) {
max_ending_here = 0
int_s = i + 1
}
}
cat("Sum is: ", max_so_far, " with starting position: ", subarray_start, " and ending: ", subarray_end)
}
# run the function
kadane_with_position(v)
Kadane’s algorithm has also an interesting time complexity function. With O(n) for an array, it can explode exponentially when using 2D matrices: O(n^3).
R library Adagio offers this function with ability to calculate over matrices.
As always, code is available at Github in the same Useless_R_function repository. Check Github for future updates.
Happy R-coding and stay healthy!“
R-bloggers.com offers daily e-mail updates about R news and tutorials about learning R and many other topics. Click here if you're looking to post or find an R/data-science job.
Want to share your content on R-bloggers? click here if you have a blog, or here if you don't.