Resource governor and external resource pool for Microsoft R Services
Want to share your content on R-bloggers? click here if you have a blog, or here if you don't.
Setting external resource pool for execution of R commands using sp_execute_external_script has proven extremely useful, especially in cases where you have other workers present, when you don’t want to overdo on data analysis and get to much resources from others (especially when running data analysis in production environment) or when you know that your data analysis will require maximum CPU and memory for a specific period. In such cases using and defining external resource pool is not only useful but highly recommended.
Resource governor is a feature that enables you to manage SQL Server workload and system resource consumption their limits. Limits can be configures for any workload in terms of CPU, Memory and I/O consumption. Where you have many different workloads on the same SQL Server, resource Governor helps allocate requested resources.
By default, two pools are defined – default and internal for system resources, and only default for system external resources.
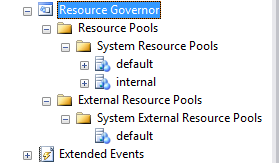
Resource governor has resource pools, workload groups that are groups of similar load within same classification criteria. When defining external resource pool we will be defining the limitations for CPU and/or memory consumption for external resources. And R Services (using external procedure sp_execute_external_script) falls under external resources. According to MSDN, with external resource pool for R services will govern “rterm.exe, BxlServer.exe, and other processes spawned by them (quoted: link)”
First of all, you need to have resource governor enabled:
-- Enable Resource Governor ALTER RESOURCE GOVERNOR RECONFIGURE; GO
Once you have this, let us set the query for test so we can measure and see how the resource governor will behave.
I will be using RevoScaleR sample data, that come with each R Service installation of SQL Server 2016. This sample data should be available on following location:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.MSSQLSERVER\R_SERVICES\library\RevoScaleR\SampleData

And I will be using AirlineDemoSmall.csv – CSV dataset, roughly 14MB size. Please note, that path to the SampleData might differ, based on your SQLServer 2016 installation folder.
In your database create and import data to your SQL Server table:
CREATE TABLE AirlineDemoSmall( ArrDelay varchar(100) NOT NULL ,CRSDepTime float NOT NULL ,[DayOfWeek] varchar(12) NOT NULL ) GO -- this file should be at your location! so no need to download it BULK INSERT AirlineDemoSmall FROM 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.MSSQLSERVER\ R_SERVICES\library\RevoScaleR\SampleData\AirlineDemoSmall.csv' WITH ( FIELDTERMINATOR = ',', ROWTERMINATOR = '\n', FIRSTROW = 2 -- Skip header )
*Please note; both statements (CREATE TABLE and BULK INSERT) are part of RevoScaleR ImportAirlineDB.sql file. I am just reusing a section of this code. Whole file will be added to Github.
Once you have your data imported, we will run a simple linear regression using RevoScale library.
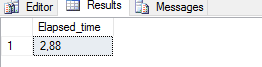
EXECUTE sp_execute_external_script @language = N'R' ,@script = N' library(RevoScaleR) f <- formula(as.numeric(ArrDelay) ~ as.numeric(DayOfWeek) + CRSDepTime) s <- system.time(mod <- rxLinMod(formula = f, data = AirLine)) OutputDataSet <- data.frame(system_time = s[3]);' ,@input_data_1 = N'SELECT * FROM AirlineDemoSmall' ,@input_data_1_name = N'AirLine' -- WITH RESULT SETS UNDEFINED WITH RESULT SETS (( Elapsed_time FLOAT ));
So I am only exporting R system time function and only Total elapsed time (hence 3 attribute from vector result of system.time function). Usual representation of this function is following format: user time, system time and elapsed time.

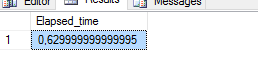
And will only take elapsed time as a measure and comparison between resource pool enabled and disabled. Results from our control environment (before setting the resource pool):

and computation time is 0.058 of a second where as elapsed time – value returned from our sp_execute_external_script – is 0,63 of a second.
Now we will create a new pool and limit the CPU and memory available for such workloads:
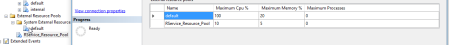
-- Default value ALTER EXTERNAL RESOURCE POOL [default] WITH (AFFINITY CPU = AUTO) GO CREATE EXTERNAL RESOURCE POOL RService_Resource_Pool WITH ( MAX_CPU_PERCENT = 10 ,MAX_MEMORY_PERCENT = 5 ); ALTER RESOURCE POOL [default] WITH (max_memory_percent = 60, max_cpu_percent=90); ALTER EXTERNAL RESOURCE POOL [default] WITH (max_memory_percent = 40, max_cpu_percent=10); ALTER RESOURCE GOVERNOR reconfigure;
New pool – called: RService_Resource_Pool is created with new values set.
And obligatory reconfiguration:
ALTER RESOURCE GOVERNOR RECONFIGURE; GO
This configuration can also be found using this system configuration table:
-- Check configuration SELECT * FROM sys.resource_governor_external_resource_pools
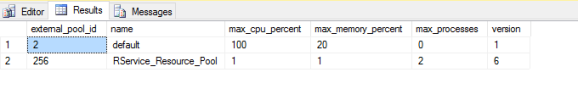
Please note that only 20 workers are dedicated to be used for R external processes.

With each run of RevoScaleR library functions an increment will appear for DMV statistics on external script execution. Also, only RevoScaleR functions are counted here. Any other function (to my knowledge) is not counted here (as of SQL Server 2016 version).
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_external_script_execution_stats

Once you have this, we need to set the Classification function as well:
CREATE WORKLOAD GROUP R_workgroup WITH (importance = medium) USING "default",
EXTERNAL "RService_Resource_Pool";
ALTER RESOURCE GOVERNOR WITH (classifier_function = NULL);
ALTER RESOURCE GOVERNOR reconfigure;
USE master
GO
CREATE FUNCTION RG_Class_function()
RETURNS sysname
WITH schemabinding
AS
BEGIN
IF program_name() in ('Microsoft R Host', 'RStudio') RETURN 'R_workgroup';
RETURN 'default'
END;
GO
ALTER RESOURCE GOVERNOR WITH (classifier_function = dbo.RG_Class_function);
ALTER RESOURCE GOVERNOR reconfigure;
go
On MSDN you will find a post on setting up resource governor for R Services and due to security reasons, “However, direct management of the Launchpad service by using Resource Governor is not supported.” So, this practically means that you can also create a login with one of twenty R User Names (MSSQLServer01 … MSSQLServer20) in group of SQLRUserGroup in order for Resource Governor to work.
So, much coding needed at this point. I will be using User MSSQLSERVER01 and create all the necessary things: logins, permissions, etc.After setting up MSSQLSERVER01 windows user and using EXECUTE AS LOGIN command prior to running sp_execute_external_script.
Running the command:
SELECT * FROM sys.resource_governor_workload_groups;
you will now see all the workload groups.
And now, finally we can rerun the same procedure:
-- We will run same query EXECUTE sp_execute_external_script @language = N'R' ,@script = N' library(RevoScaleR) f <- formula(as.numeric(ArrDelay) ~ as.numeric(DayOfWeek) + CRSDepTime) s <- system.time(mod <- rxLinMod(formula = f, data = AirLine)) OutputDataSet <- data.frame(system_time = s[3]);' ,@input_data_1 = N'SELECT * FROM AirlineDemoSmall' ,@input_data_1_name = N'AirLine' -- WITH RESULT SETS UNDEFINED WITH RESULT SETS (( Elapsed_time FLOAT ));
And CPU consumption will stay within the limits:
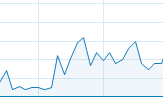
and the elapsed time will be higher due to lower CPU available.
Happy R-Tsqling!
Code Is available at Github.
NOTE!
CPU consumption will rise after the execution of external execution command due to the worker MSSQLSERVER01 cleaning the session files and log files!
Since log and session files are part of Launchpad service, Resource Governor will not be able to limit the CPU, Memory of I/O consumption.
R-bloggers.com offers daily e-mail updates about R news and tutorials about learning R and many other topics. Click here if you're looking to post or find an R/data-science job.
Want to share your content on R-bloggers? click here if you have a blog, or here if you don't.
